Up to 80% of people suffer from low back pain.For some it may be one or more episodes of life, while for others the pain becomes chronic.There are many reasons that cause pain, so for an accurate diagnosis you should definitely consult a doctor.Each condition must be considered individually to ensure appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
What causes pain
The likelihood of developing back pain increases due to a number of factors.
Age and poor physical fitness
The first lower back problems are felt between the ages of 25 and 45.With age, pain tends to intensify and become chronic due to the aging of the spine.
If the muscles that support the spine are not sufficiently developed and strengthened, this can lead to spinal diseases.Lower back pain often occurs in physically unprepared people who have lifted a heavy object.
Excess weight and heredity
Obesity places additional stress on the lumbar region.
There is a genetic predisposition to diseases.For example, if one of your relatives has a history of spondylosis or radiculitis, you may be susceptible to the same conditions.
Working conditions
If your job involves lifting heavy objects, you could hurt your back.Additionally, prolonged sitting can lead to lower back pain, especially in a person with poor posture.
Backpack
Try weighing your child's backpack.If it weighs more than 20% of the child's weight, wearing it causes muscle tension and back pain.
Other domestic reasons
Back pain can occur during daily activities:
- lift a heavy box, carry heavy shopping bags;
- rearranging furniture;
- lifting weights in the gym;
- turning your back during sporting activity (golf, tennis, contact sports);
- during agricultural and construction work.
Spine problems, radicular pain and herniated disc
A common cause of back pain is a disease or injury to the muscles, bones and/or nerves of the spine.
Radicular pain appears due to pinching, hernia, when direct irritation of the nerve occurs.For example, in sciatica, the pain syndrome is acute, accompanied by numbness in the leg area, which is innervated by the affected nerve.
Hernias develop when the spine degenerates or thins.The central gelatinous portion of the disc protrudes from the central cavity and extends away from the nerve root.Intervertebral discs begin to degenerate by the 3rd decade of life.Herniated discs occur in one-third of people over the age of 20.However, only 3% of them cause lower back problems.
Spondylosis and narrowing of the spinal canal
It occurs when the intervertebral discs lose moisture and volume with age, causing the disc height to decrease.Even minor trauma with spondylosis can cause inflammation and damage to the nerve root.This can lead to classic sciatica without disc rupture.
Spinal disc degeneration combined with lower back joint disease can lead to a narrowing of the spinal canal.These changes cause pain.The narrowing of the canal is clearly visible on an x-ray.A person with spinal stenosis may have low back pain that radiates to both lower extremities.Symptoms may worsen after standing for a long time or walking even short distances.
Cauda equina syndrome and musculoskeletal pain syndromes
This is an emergency condition in which the spinal cord itself becomes compressed.The disc expands into the spinal canal, which compresses the nerves.The person is bothered by pain, possible loss of sensation, intestinal or bladder dysfunction.This can lead to an inability to control urination: there may be urinary incontinence or an inability to start urinating.
Musculoskeletal pain syndromes cause significant symptoms and include myofascial syndromes and fibromyalgia:
- Myofascial pain is characterized by tenderness in localized areas (trigger points).The range of motion in the affected muscle groups decreases.Relief often occurs when the affected muscle group can be relaxed.
- Fibromyalgia causes widespread pain and tenderness throughout the body.Patients are concerned about general tension, fatigue and muscle stiffness.
Muscle or ligament strain, protruding or ruptured discs
Repeated lifting of heavy objects or sudden, awkward movements can strain the muscles of the back and spine.If a person is in poor physical condition, constant stress on the back can cause painful muscle spasms.
The discs act as cushions between the bones of the spine.The soft core of the disc can swell or rupture and put pressure on the nerve.But it is possible to have a bulging or ruptured disc without back pain.The disease is often discovered by chance when an x-ray of the spine is taken for some other reason.
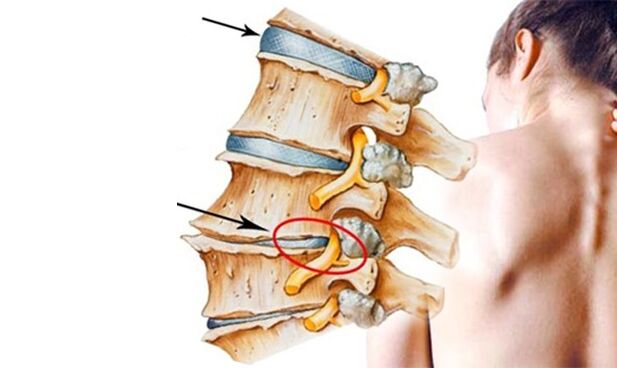
Arthritis, arthrosis and osteoporosis
Osteoarthritis can affect the lower back.In some cases, arthritis of the spine can cause the space around the spinal cord to narrow.This condition is called spinal stenosis.
Osteoporosis of the spine can cause compression fractures if the bones become porous and brittle.
Spondylolisthesis and skeletal pathologies
A condition in which a bone in the spine falls or moves from its normal position.This can cause lower back pain and stiffness, as well as numbness and tingling in the extremities.
Skeletal disorders, a condition in which the spine curves sideways (scoliosis), can also lead to back pain.It typically occurs before middle age.
Infectious inflammatory processes
Bone infections (osteomyelitis) of the spine are a rare cause of low back pain.Inflammation of the nerves in the spine can occur when the nerves become infected by the shingles virus, which causes shingles.It can occur in the thoracic region, causing symptoms in the upper back, or in the lumbar region, causing lower back pain.
Spondylitis can cause stiffness and pain in the spine, which is especially worse in the morning.Ankylosing spondylitis usually begins in people during adolescence and young adulthood.
Tumors and other causes
Benign and malignant tumors (as well as metastases) can cause lower back pain.
Pain that occurs due to organ abnormalities within the abdomen, pelvis, or chest may also be felt in the back.For example, appendicitis, aneurysms, kidney disease, kidney infections, bladder and pelvic infections, and ovarian disease can cause lower back pain.This pain is not associated with physical activity and comes on suddenly.If it appears, you should urgently contact a medical facility or call an ambulance at home.A normal pregnancy can also cause back pain.While carrying a baby, you may feel pelvic tightness, nerve irritation, and tension in your lower back.
Prevent back pain
For prevention, experts recommend the following methods:
- Exercise regularly.Moderate exercise is suitable: walking, swimming or cycling for 30 minutes a day.Yoga helps remove muscle tension, strengthen muscles and improve posture.
- Before working out, exercising at home or working in the garden, do a short warm-up with stretching.
- Do not arch your lumbar spine or lean when standing or sitting.Poor posture increases stress on the lower back.
- At home or at work, ensure that work surfaces at home or at work are at a height that is comfortable for you.The chair should support your back well.Don't sit for too long, take a break periodically to walk around.
- Wear comfortable shoes with low heels.
- Sleeping on your side with your knees slightly bent can help open the joints in your spine and relieve pressure, reducing the curvature of your spine.
- Try not to lift too heavy objects.If you have to carry weights, you have to lift them by pushing yourself with your feet.You cannot bend or straighten your back: it must remain straight.
- Don't overeat to maintain optimal weight.To support the skeletal system, an adequate intake of calcium, phosphorus and vitamin D is necessary.
- Stop smoking.Smoking reduces blood flow to the lower spine, which can contribute to the development of degenerative processes.
When to see a doctor
If you associate the onset of back pain, for example, with lifting heavy objects, then after rest your health will be restored.You can take a painkiller.
You need to see a doctor if:
- the pain does not go away for several days or becomes more intense;
- there is irradiation in the abdomen or radiates to the legs;
- increased body temperature;
- there was severe lethargy and weakness;
- if you have recently had severe weight loss for no apparent reason;
- defecation and urination have become uncontrollable and spontaneous;
- a sports, automotive, or home injury occurred.
As you can see, the list of reasons why back pain in the lumbar region is extensive.In less than 1% of people, the cause of back pain is a tumor, infectious processes or problems with internal organs.




















